PlugMapper Insights
NEMA 14‑50 vs 6‑50 for EV Charging: Which Outlet Should You Install?
A homeowner’s guide to choosing between NEMA 14‑50 and 6‑50 for Level 2 EV charging—wiring, breakers, code tips, and real‑world use.
EV Charging Stations Editorial Team8 min read
home chargingNEMA 14-50NEMA 6-50electricalLevel 2
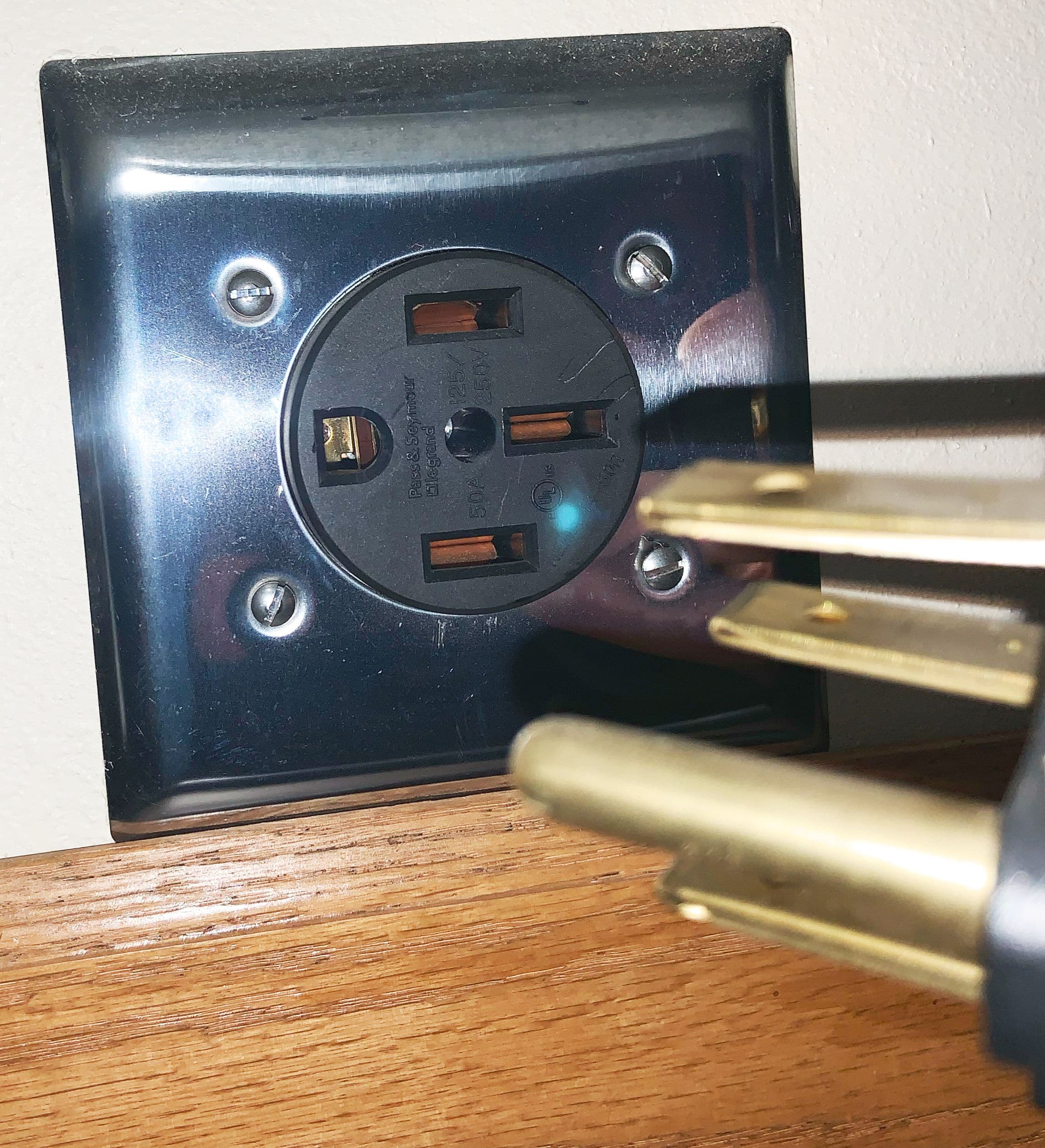

Both NEMA 14‑50 and 6‑50 are common 240‑volt outlets for Level 2 charging. The 14‑50 includes a neutral conductor; the 6‑50 does not. Here’s how to decide which fits your garage and charger.
Quick differences
- NEMA 14‑50: two hots + neutral + ground (4‑wire).
- NEMA 6‑50: two hots + ground (3‑wire), commonly used for welders.
- Most EVSEs don’t need neutral—but some accessories or multi‑use circuits might.
Panel & breaker sizing
Most 40A continuous EVSEs specify a 50A breaker. Use appropriately sized copper conductors and a properly rated receptacle/enclosure. Follow manufacturer instructions and local code.
When to pick each
- Choose 14‑50 if you want flexibility for appliances or future devices that require neutral.
- Choose 6‑50 if your EVSE plug is 6‑50 and you want a simpler 3‑wire run.
- Consider hardwiring for highest reliability in harsher or outdoor locations.
Safety first: use a listed receptacle, torque terminations to spec, and avoid cheater adapters that can overheat.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Do I need GFCI for a garage outlet?
A: Many jurisdictions require it—check your local code and EVSE manual.
Q: Will a 14‑50 charge faster than a 6‑50?
A: No—the speed depends on the EVSE amperage and your vehicle’s onboard charger.
Enjoyed this story? Browse more insights on the PlugMapper blog.Talk to our team

